Build DrCCTPorf Instrumentation Clients
We go through an example to show how to create, build, and run a DrCCTProf client.
Basic structure of a client
This section describes the basic structure of a DrCCTProf client, including the functionality of various events occurring during the program execution.
DrCCTProf is developed atop DynamoRIO. It collects the call path of every binary instruction at runtime. It provides a rich set of APIs for developers to build instrumentation clients. The term ‘instrumentation client’ in this context refers to a shared object file that uses the DrCCTProf APIs & DynamoRIO APIs to analyze desired instructions (e.g., all instructions, memory accesses, or branches) at runtime.
To work on the libdrcctlib_instr_statistics_clean_call.so client, you must understand its implementation in instr_statistics_clean_call.cpp. The diagram below shows the key functions in instr_statistics_clean_call.cpp and how they relate to each other.
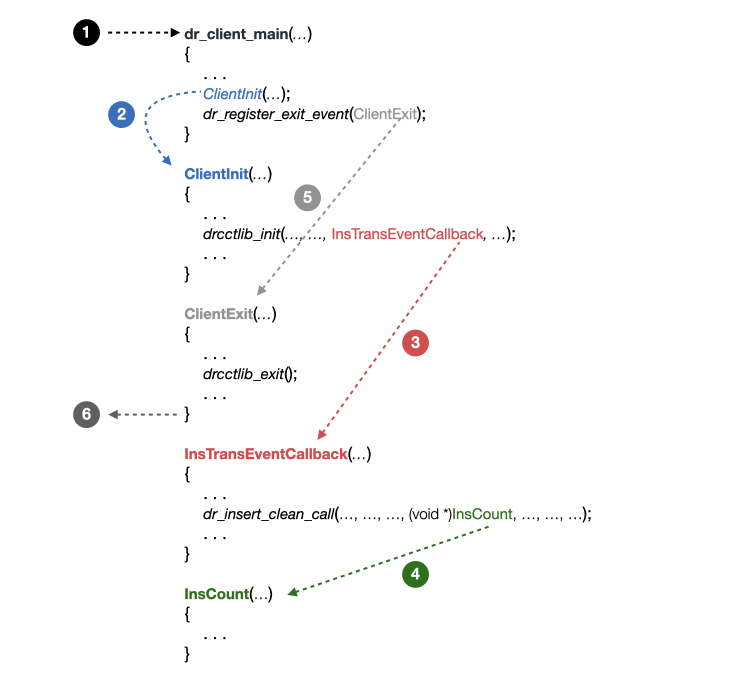
The easiest way to understand the client is to think of it as event driven. Each function is called upon the occurence of an event during the application execution:
DynamoRIO loads and runs the client, calling
dr_client_main()before the application execution.
In
dr_client_main(), the client callsClientInit(), which initializes any extensions of DynamoRIO before the application execution.
In
ClientInit(), the client callsdrcctlib_init(), which initializes DrCCTPorf and registers a function (InsTransEventCallback()) at each instruction in the application before the application execution. Such a function register for an event (i.e., upon each instruction) is usually called as a ‘callback function’.
In
InsTransEventCallback(), the client registers a callback function (InsCount()), which is executed upon each application instruction. TheInsCount()function is used to collect and analyze instruction-level information, which typically requires the most coding efforts.
In
dr_client_main(), the client registers a callback function (ClientExit()), which is invoked just before the client stops running (i.e., at the end of the application execution).
The application stops running and DynamoRIO calls ClientExit(), where one can output the analysis results..
The steps above simply explain the mechanism for a DrCCTProf client. For detailed information, read the instr_statistics_clean_call.cpp file, and refer to details of key functions in the DynamoRIO functions and DrCCTProf APIs reference manual, especially: dr_insert_clean_call(), which implements the instrumentation and drcctlib_init(…, …, InsTransEventCallback, …), which defines where the
instrumentation must be inserted.
Code Transformation and code Execution
If you are new to the Dynamic Binary Instrumentation (DBI) tool platform in general, and DynamoRIO in particular (DynamoRIO is a DBI tool), ensure you understand the instrumentation mechanism for the application being monitored.
Remember that instrumentation occurs in two phases, transformation and execution:
Transformation
Instrumentation code is inserted into the application code. This is only executed once before the application execution.
Execution
The instrumentation code (inserted in the transformation phase) runs together with the application code on the fly.
DynamoRIO performs transformation and execution phases transparently, following the rules of its APIs.
In the above example, InsTransEventCallback() is in the transformation phase, which inserts InsCount() function before each application instruction. Note that InsCount() is not invoked at this phase.
At the execution phase, when an application instruction is executed, InsCount() is invoked to count instruction statistics.
The best way to distinguish the two phases is to understand that dr_insert_clean_call() is called once when an application instruction is transformed, but the function it instruments may be called many times when the application instruction is executed.
Add a new client to DrCCTProf build system
If you want to add a new client, you need to create a folder with the client name in DrCCTProf/src/clients, and put the client_name.cpp and CMakeLists.txt in it. Then, when you finish the programming, you can run “sh build.sh” in the DrCCTProf root directory to build it. One can refer to any of the example clients to see how to edit the CMakeLists.txt.